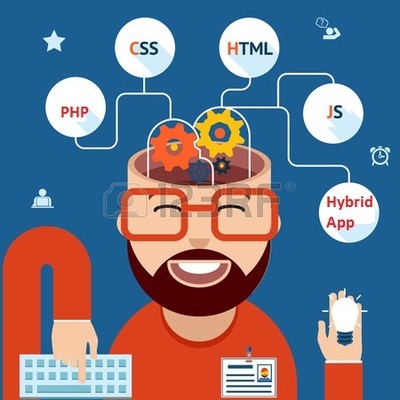
Web Developer Fields
Back End Developer
The back end of a website consists of a server, an application, and a database. A back-end developer builds and maintains the technology that powers those components which, together, enable the user-facing side of the website to even exist in the first place. In order to make the server, application, and database communicate with each other, back-end devs use server-side languages like PHP, Ruby, Python, Java, and .Net to build an application, and tools like MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server to find, save, or change data and serve it back to the user in front-end code. Job openings for back-end developers often also call for experience with PHP frameworks like Zend, Symfony, and CakePHP; experience with version control software like SVN, CVS, or Git; and experience with Linux as a development and deployment system. Back-end devs use these tools to create or contribute to web applications with clean, portable, well-documented code. But before writing that code, they need to collaborate with business stakeholders to understand their particular needs, then translate those into technical requirements and come up with the most effective and efficient solution for architecting the technology.



